Genes & Cancer
Correction: Inhibitory effect of miR-377 on the proliferative and invasive behaviors of prostate cancer cells through the modulation of MYC mRNA via its interaction with BCL-2/Bax, PTEN, and CDK4
Yasamin Azimi1, Sara Hajibabaei1, Ghazal Azimi2, Fatemeh Rahimi-Jamnani3 and Masoumeh Azizi1
1Department of Molecular Medicine, Biotechnology Research Center, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran
2Department of Nanotechnology, Tehran Medical Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
3Department of Mycobacteriology and Pulmonary Research, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: Masoumeh Azizi, email: mazizi528@gmail.com, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4679-3248
Published: January 29, 2025
Copyright: © 2025 Azimi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
CORRECTION
Original article: Genes&Cancer. 2024; 15:28–40. https://www.genesandcancer.com/article/236/pdf/
PMCID: PMC11098572 PMID: 38756697;
DOI: 10.18632/genesandcancer.236
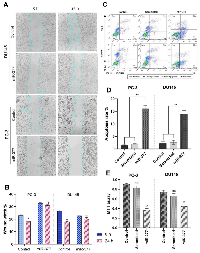
The corrected version of the text of the article chapter and Figure 3 are provided below.
Overexpression of miR-377 induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines due to MYC down-expression
The impact of miR-377 on apoptosis in PC-3 and DU145 cells was assessed using annexin V and PI in flow cytometry. Compared to controls, the findings showed a rise in the number of cells going through early apoptosis. As shown in (Figure 3C, 3D), control cells for this experiment included un-transfected cells and cells transfected with scrambled oligonucleotides. In cells transfected with miR-377 compared to controls, the apoptosis ratio increased considerably. The percentage of early apoptotic cells increased from 1.05% to 16.6% in PC-3 and from 1.66% to 14.5% in DU145 transfected with miR-377.
- 1. Targeting long non-coding RNA MALAT1 reverses cancerous phenotypes of breast cancer cells through microRNA-561-3p/TOP2A axis. Sci Rep. 2023; 13:8652. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35639-x. [Pubmed]